Answer to Quiz: Pacemaker on page 130 and case discussion
QUIZ
Answer to Quiz: Pacemaker on page 130 and case discussion
Article Summary
- DOI: 10.24969/hvt.2018.88
- Page(s): 133-134
- Electrophysiology
- Published: 26/10/2018
- Received: 25/10/2018
- Views: 7934
- Downloads: 8209
- Keywords: quiz, electrocardiogram, pacemaker
Address for Correspondence: Mykhaylo Sorokivskyy, Lviv Regional Cardiology Center, Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine
Email: msorokivskyy1@gmail.com
Correct answer D
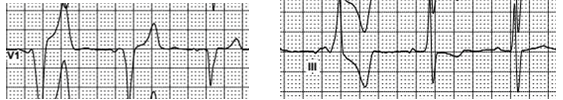
D) 1,2 – atria: paced rhythm, ventricles: impulse conducted via AV node with RBBB;
3 – atria: premature beat, ventricles: impulse conducted via AV node with RBBB;
4,5 – atria:paced rhythm, ventricles: paced rhythm;
6 – atria and ventricles – fusion beat;
7,8 – atria and ventricles – sinus rhythm with incomplete LBBB.
1,2 – atria: paced rhythm
Clear spike of pacemaker is visible before P-wave of the 2nd PQRST. The shape of 1st P-wave is equal to 2nd and interval between P-wave peaks of the 1st and 2nd is 1000 msec. So, heart rate is 60 bpm, typical for pacemaker setting.
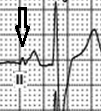
1,2 – ventricles: impulse conducted via AV node with RBBB.
A paced QRS morphology usually has a LBBB morphology when the lead is located in the RV. Configuration of RBBB in this case is a sign of native AV conduction with underlying RBBB.
3 – atria: premature beat
Early appearance and different (from sinus rhythm) configuration of the 3rd PQRST complex P-wave is characteristic of the atrial premature beat.
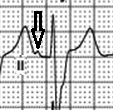
3 – ventricles: impulse conducted via AV node with RBBB
The same as in 1,2 complexes
4,5 – atria: paced rhythm
Small pacemaker spike is visible before P-wave of the 4th and 5th PQRST. The shape of P-wave of these complexes is equal to 2nd and interval between P-wave and R-wave peaks of the 4th and 5th is 1000 msec.
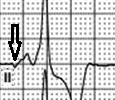
4,5 – ventricles: paced rhythm
QRS complex is induced by pacemaker and has LBBB configuration. AV delay (interval between spike of atrial electrode and start of QRS) is near 160 ms and it`s common to DDD pacemakers settings. Spike of ventricle electrode is invisible due to bipolar mode of pacing.
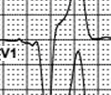
The configuration of the 6th PQRST is intermediate between 5th and 7th. This statement concerns to all ECG elements: P- wave, QRS complex and T-wave. “Fusion”- means that atria are partially excited from sinus node and partially from pacemaker electrode (tiny spike is clearly seen in leads V3 and V4). Ventricles also are partially excited by impulse conducted via AV node and partially from ventricular lead.
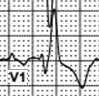
7,8 – atria sinus rhythm
P-wave is positive in lead II and biphasic in lead V1 – generally suggesting a sinus node origin / sinus P wave. Spike of atrial electrode that was visible in prior complexes is unseen before 7th and 8th P-waves
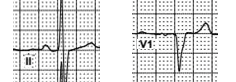
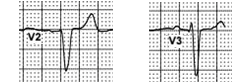
7,8 – ventricles – sinus rhythm with incomplete LBBB.
Practically normal configuration of the QRS complex means that impulse was conducted normally via AV node. Absence of the RBBB configuration of the QRS means that right branch bundle block is transient in this patient. QRS duration of ~ 110 ms (the best noticeable in V2) and low R-wave voltage in V3 are the characteristics of incomplete left branch bundle block.
Comment
The shape of the 4th and 5th QRS complexes is conditioned by the placement of the ventricular electrode near the right ventricle outflow tract. It is not usual location of the ventricular electrode.
The considerable difference between the PQ interval duration in the 2nd and the 4th PQRST complexes can be explained by collaboration of two pacemaker algorithms. The atrial premature beat of the 3rd PQRST complex leads to switching on the PMT (pacemaker mediated tachycardia) intervention. Work of this mechanism can blind the 3rd QRS complex for pacemaker. Accordingly, the absence of the QRS after P-wave triggers MVP (Managed Ventricle Pacing) algorithm, which leads to the notable shortening of the PQ interval in the 4th PQRST complex. The MVP algorithm foresees slight PQ interval prolongation in the following complexes, which can be noticed in the 5th and 6th QRS complexes.
Mykhaylo Sorokivskyy
Lviv Regional Cardiology Center,
Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine
Peer-review: Internal
Conflict of Interest: None to Declare;
Authorship: M.S.
Acknowledgement and funding: None to declare
Copyright

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
AUTHOR'S CORNER

